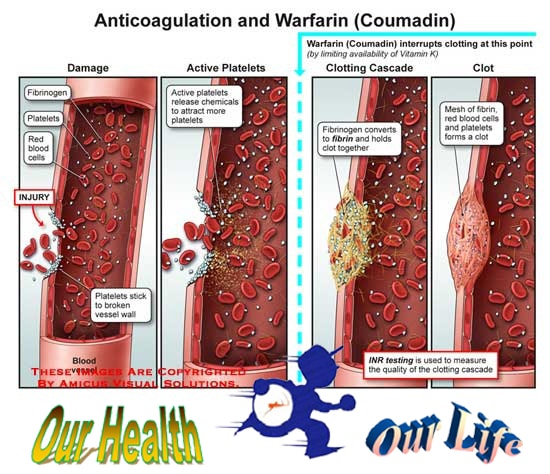
The Anticoagulated:
Oral anticoagulants are indicated in the long-term prevention of thromboembolic disease, ie in all those clinical situations that they are associated with high incidence of thromboembolism and in cases in which the first symptom of the disease is thrombotic accident or embolic to prevent the second. They are also used in the short term after a first episode of DVT or pulmonary embolism.
The major complication that can result from treatment with oral anticoagulants is bleeding as to prevent thrombosis or embolism have to get a blood hypocoagulability.
Interactions with other drugs anticoagulants.
There are significant interference with other drugs, can be enhanced or slow down the action of the anticoagulant. The list of drugs that interact is very extensive. In principle not be taken or antiplatelet (Aspirin, Adiro®) or anti-inflammatory.
[ads]
General advice.
ON THE DRUG.
- Ensure that the brand and dose per tablet of the drug is going to take are the same as those indicated by the doctor.
- Take the prescribed dose and the exact number of indicated doses.
- Not increase or reduce the dose if you forget it without checking.
- Always take home medicine box.
- Control of anticoagulant therapy should be done at least every 4 or 5 weeks.
- Always take the time card.
- Do not use intramuscular injections or prior consultation if the use of these were essential.
- The orange color of the urine is normal during treatment.
- Keep the medicine out of reach of children.
LIFE ON THE REGIME.
- Do not make major changes in diet and not add or remove medicines without doctor’s advice.
- Do not abuse alcohol or fats. Do not drink beer. You can drink wine in moderation and within meals.
- Avoid oily laxatives.
- Do not take aspirin or medicines that contain it.
ON DISEASES.
- In case of illness with or without fever, diarrhea, loss of appetite, or jaundice contact your doctor.
- Every disease can modify the therapeutic range, in these cases, the controls will be most needed.

What should you do before a bleeding?
If you bleed for no reason, bleed more than normal or you bruise spontaneously, they need to seek medical control center before the date indicated in its license had anticoagulation. Keep in mind that the anticoagulated patient has no spontaneous bleeding, because the hemostatic system is generally intact, and therefore have to find the cause of the bleeding, for example if there is blood in the urine will have to rule out a urinary tract infection or if you have bloody stools should be ruled gastrointestinal bleeding, etc …
Never, as a first step, we must suspend anticoagulant therapy, you need to always go to a medical center, if outside of working hours go to the ER.
If bleeding is not too heavy it will not be necessary to advance the control even if it will be necessary to comment on it at the next visit. If bleeding is more abundant or lasts longer if it will be necessary to advance the control and adjust the dose to achieve the cessation of bleeding.
- Conjunctival hemorrhage: often due to capillary fragility aggravated by sneezing, coughing fit … not required overtreatment.
- Nosebleeds (epistaxis) usually happens due to nasal congestion, when the environment is very dry and the mucus is dry because it is hot, because it sounded strong … As a therapeutic extent could the implementation of a cap with a local hemostatic. It is convenient blow your nose immediately after the morning washing. It can be prevented by applying Vaseline on both nostrils and humidifying the air in the room.
- Gingival: the gum is a soft tissue that bleeds easily, the buco-dental cleaning should be frequent and careful brushing helps strengthen the gums.
- Skin haematomas: usually occur by capillary fragility. If they are of low intensity you will not need to do anything, if they have to do a great control.
- Bloody sputum: often it is blood from the throat. It will be necessary to perform a visual examination.
- Red blood in the stool: if you are constipated may be due to the presence of hemorrhoids or anal fissure. We will have to perform a proper examination. You must notify the control to adjust the dose and / or prevent anemia.
- Gynecological hemorrhage (small quantity): if in near menopause age will be caused, in most of the time, by hormonal disorders. You will need a gynecological exam performed.
Hemorrhage requiring urgent assistance.
They are those that by their location or amount of blood loss can compromise the patient’s life or performance of blood transfusion should be needed. Often require the cessation of anticoagulant therapy.
- Sudden blindness.
- Epistaxis (nosebleeds) that can not be stopped.
- Severe headache with vomiting.
- Hemoptysis (coughing up Sange) and hematemesis (vomiting blood).
- Acute abdomen.
- Manes. They are pasty stools black and color.
- Severe gynecological haemorrhages.
- Blood in urine.
What should you do if you have a fever?
Anticoagulated fever in a patient, as in other person not taking an anticoagulant, is often a symptom of an infectious disease. If the fever is caused by a viral infection need be taken only as antipyretic paracetamol (do not use aspirin or medicines containing it). There are also physical to try fever is reduced such as applying cold compresses or warm bath measures.Antibiotics should only be used in case of bacterial infection and always prescribed by your doctor.
What should you do if you have pain?
If an anticoagulated patient has pain can take a painkiller paracetamol or metamizol type. The route of administration are chosen according to the intensity, discarding intramuscularly because of the danger of bleeding which itself carries the puncture.
If the pain is to articulate such measures should be attempted as dry heat, massage on the area, an anti-inflammatory ointment and practice rehabilitation exercises.
What should you do if you are pregnant?
If a patient with an oral anticoagulant treatment of reproductive age become pregnant should be contacted as soon as possible with the doctor responsible for the control treatment in order to avoid the harmful effects of oral anticoagulants since they are able to cross the placental barrier and produce fetal malformations.
What to do if you injure yourself?
The patient taking anticoagulants and traumatized, with open wound should know that your blood takes longer to clot so should make a more prolonged compression of the area. If the wound is large in size and amount of blood it must be sent to an emergency service.
If the patient suffers an injury without open wound must immediately performed a compression bandage. The compression must be maintained 12 hours, taking care not to cause a secondary ischemia.
If there is bone fracture should be taken immediately to an emergency room.
What should you do if you have to go to the dentist or undergo surgery?
An anticoagulated patient can not undergo tooth extraction NEVER without taking adequate to reduce the risk of bleeding measures.
Patients who are anticoagulated because they carry a prosthetic valve or have uncorrected valvular disease, should not stop anticoagulation never, so to be treated in a hospital where they can be adequate hemostasis after extraction.
If patients are anticoagulated because they suffered a venous thrombosis, pulmonary embolism or have an arrhythmia it is sufficient to suspend the doses about two days before, but it is not advisable to make more than one withdrawal per month.
If after extraction bleeding happens you should go to the dentist to try to stop the bleeding.
If you are going to have surgery, you notify your doctor. It is necessary to know the date thereof at least one week in advance to properly preparrlo.
What to do if you should be vaccinated?
The anticoagulated patient has the same indications of vaccination as a healthy person, besides the risk of infectious disease is greater than that of the normal population and may unbalance the disease.
The administration of any vaccine should be evaluated by your doctor. The route of administration is not contraindicated, either orally or subcutaneously. The injection of tetanus vaccine, which is an intramuscular injection, should preferably be placed on the arm.